octave tutotial 3
Tags: octave
Control Statements: for, while, if statement
- for loop
v = zeros(10, 1) v = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 for j = 1 : 10, v(i) = 2 ^ i; end; v v = 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512 1024 - for loop 2
好還要更好 ! 就是一直修正~~~ 接下來的 code example 都會直接把 octave code 畫面剪下來貼上去
 所以可以看的到 » 唷唷
所以可以看的到 » 唷唷>> indices = 1 : 10; >> indices indices = 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 >> for i = indices, disp(i); end; 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 - while
>> v v = 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512 1024 >> i = 1; >> while i <=5, v(i) = 100; i = i + 1; end; >> v v = 100 100 100 100 100 64 128 256 512 1024 - if, break
>> v v = 100 100 100 100 100 64 128 256 512 1024 >> i = 1; >> while true, v(i) = 999; i = i + 1; if i == 6, break; end; end; >> v v = 999 999 999 999 999 64 128 256 512 1024 - else if
>> v(1) = 2 v = 2 999 999 999 999 64 128 256 512 1024 >> if v(1) == 1, disp('The value is one '); elseif v(1) == 2, disp('The value is two'); else disp('The value is not one or two.'); end; The value is two - function
-
新建一個檔案, 命名 [functionName].m
% squareThisNumber.m function y = squareThisNumber(x) y = x^2 - cd 到 有這支檔案的路徑
-
EX: E:\Coursera\Machine_Learning\_octave_exercise
>> ls Volume in drive E is DATA Volume Serial Number is F859-A48F Directory of E:\Coursera\Machine_Learning\_octave_exercise [.] [..] squareThisNumber.m test.txt 2 File(s) 238 bytes 2 Dir(s) 961,864,597,504 bytes free - 直接在 octave cmd 裡呼叫使用
>> squareThisNumber(2) y = 4 ans = 4
-
- Octave search path
- 加入path 讓 octave cmd 可以無痛讀取相關檔案
- EX:
>> addpath('E:\Coursera\Machine_Learning\_octave_exercise') >> >> cd 'C:\' >> squareThisNumber(5) y = 25 ans = 25
- costFunctionJ
- costFunctionJ.m:
-
複習照片:
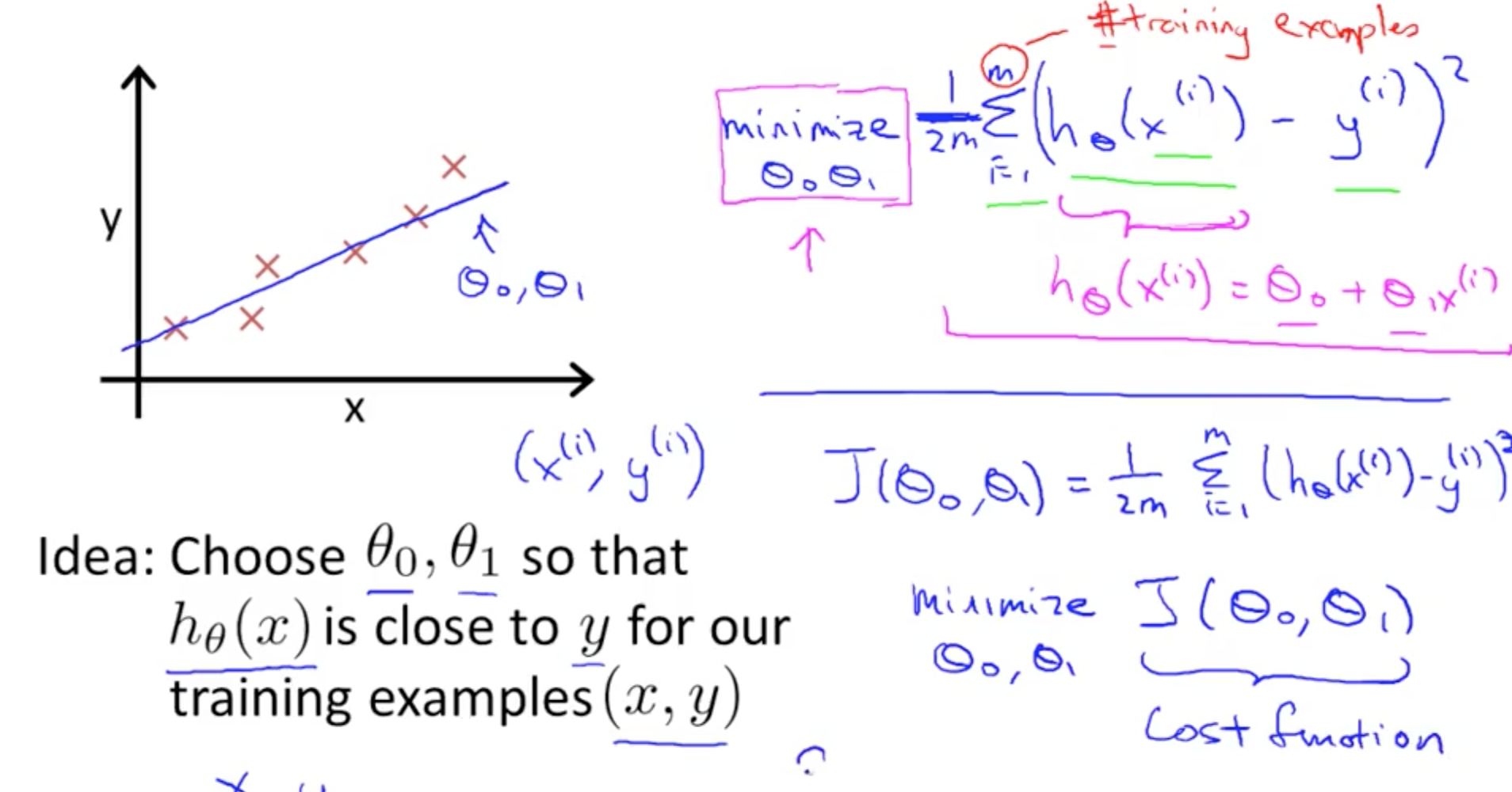
function J = costFunctionJ(X, y, theta) % X is the "design matrix" containing our training examples. % y is the class labels m = size(X, 1); % number of training examples predictions = X * theta; % predictions of hypothesis on all m examples sqrError = (predictions - y) .^2 % squared errors J = 1/(2 * m) * sum(sqrErrors); - 跑跑看 costFunctionJ:
>> X X = 1 1 1 2 1 3 >> y = [1; 2; 3] y = 1 2 3 >> theta = [0; 1] theta = 0 1 >> j = costFunctionJ(X, y, theta) j = 0 % 0 代表 完美的找出theta !!!
Vectorization
- Vectorization example
hθ(x) = ∑(j=0, n) θj * xj = θ^T * x | θ0 | | x0 | θ = | θ1 | x = | x1 | | θ2 |, | x2 |- Unvectorized implementation
prediction = 0.0; for j = i : n+1, prediction = prediction + theta(j) * x(j) end; - vectorized implementation
prediction = theta' * x;
- Unvectorized implementation
-
C ++ Vectorization example
- Unvectorized implementation
double prediction = 0.0; for( int j = 0; j <=n ; j++) prediction += theta[j] * x[j]; - vectorized implementation
double prediction = theta.transpose() * x;
- Unvectorized implementation
- Gradient descent
θj := θj - α * 1/m * ∑ ( hθ * ( x^(i) ) - y^(i) )* xj^(i) # [∑ i=1, m] (for all j)
Simultaneous update :
θ0 := θ0 - α * 1/m * ∑ ( hθ * ( x^(i) ) - y^(i) )* x0^(i) # [∑ i=1, m] θ1 := θ1 - α * 1/m * ∑ ( hθ * ( x^(i) ) - y^(i) )* x1^(i) # [∑ i=1, m] θ2 := θ2 - α * 1/m * ∑ ( hθ * ( x^(i) ) - y^(i) )* x2^(i) # [∑ i=1, m]