aiacademy day1 隨選筆記
靠邀根本在練速打 XDDD
Alan Turing
-
Mathematicain, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, theoretical biologist, and computer scientist.
-
The father of theoetical computer science and artificial intelligence
Turing Test (1950)
-
If tester cannot distinguish a machine and a man, this machine can be considered to have “intelligence”.(First time to use)
-
“Imitation Game”
-
AlphaGo as “Master” in end of 2016
-
Google Assistant in 2018 Foogle I/O
| Strong AI | Weak AI |
| General task (AGI=Artifical General intrlligence) | Specific task |
History: AI in NN
AI: Categories
- can be understood ?
- Symbolic AI:
- Intelligence comes from Human-dfiened Ruile(formal logic)
- Human can understand adn “explain mathematically”
- Human Rule <= Human Language <= Symbol => Symolic AI
- Rule-Base
- Intelligence comes from Human-dfiened Ruile(formal logic)
- Symbolic AI:
- can be gained via learning ?
- Computational Intelligence
- Intelligence come from Machine Computation
- Human can’t understand nor “explain …”
- Use “Evolutionary Algorithm” as example
- No “rule”
- Computation usually links to “learning” and “training”
- Example: Nerual Network, Fuzzy logics, Genetic Algorithm…
- Connectionism VS. Symbolimd
- Intelligence come from Machine Computation
- Computational Intelligence
![]()
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
- ML- Perspective 1: Human Behavior (1/2)
- Our daily life, we repeat an action: use knowledge to make a decision
- We expect: make a good decision
- How to mae a good decision: learn
- Prior-learning
- Post-learning
- How to adjust our knowledg:
- know gap between good and bad decision
- Eliminate the gap by adjusting knowledge
- ML - perspective 1 : Human Behavior (2/2)
- knowledge, Decision, Learn, Gap, Eliminate
- knowledge = Intelligence = Model: ML or DL
- Gap = Difference/Delta = Error/Residual = Loss Function (Objective)
- Eliminate = Minimize/Optimize: Gradient Descent or Close-Form
- Eliminate Gap = Learn = Train
- prior-learning
- post-learning
- Deep Learning
- Classic Machine Learning: example
- Decision Tree
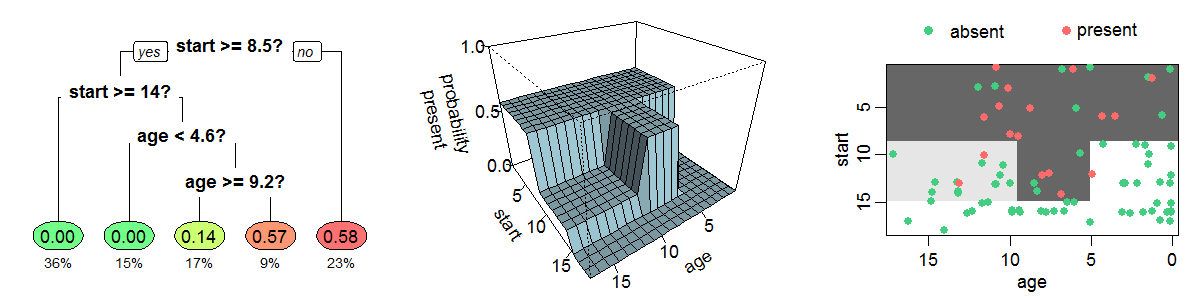
- Decision Tree
- Classic Machine Learning: example
- ML- Perspective 2: Problem Solving
- Problem, Data, Model
- ML- Perspective 3: Software
flow(algorithm),
input --> Parameters, ---> Output
Working Data
- Software => Algorithm
- 機器學習演算法是一個 解決問題的架構
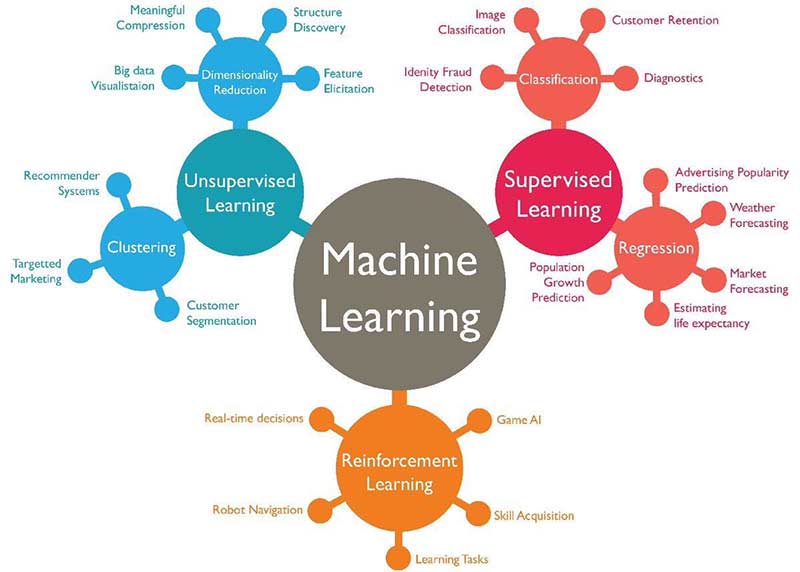
Type of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning
- Regerssion
- calssification
- Unsupervised Learning
- Clustering
- Dimensionality Reduction
- Reinforcement Learning
-
There are many Method, Approach and Algorithm to realize each Type of Machine Learning. Like DL as below:
- SL: DNN, CNN, RNN
- RL
- UL: GAN*
Machine Learning Summary
- SL, UL, RL
- Problem to REsolve
- Approach
- Deep Learning: DNN, CNN, RNN, GAN, RL
DL : NN Models / ANN (DNN)
- ANN: artifical neural network
-
DNN: Deep neural network
-
Artifical Neural Network (ANN)
-
Topolog
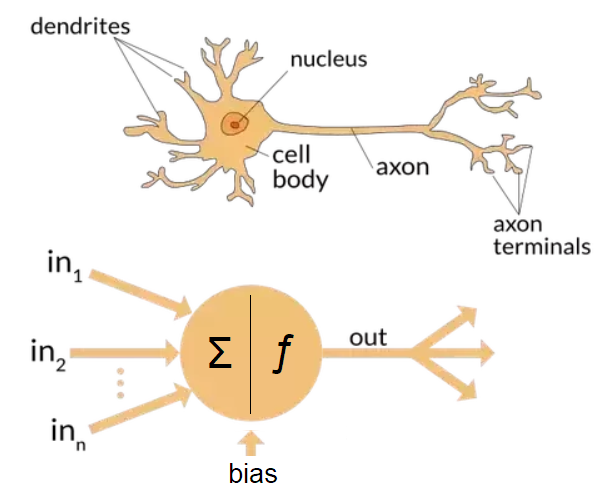
- Decide (Predict or Inference)
- x = input
- w = weight
- b = bias
- Activation Func
- y = output
- y1, y2,
- Decide (Predict or Inference)
-
Learn (Train)
- learning: designated inpur, desired output
- Use simplified single perceptron as examle
- No activation function and treat bias as constant
- y1 = x1…..
Learn: Symbolic => Numerical
- 數值分析(numerical analysis): 不是求最正確的答案,而是在合理的範圍(資源、時間等...)下求最合理的解。
Learn: Minimize
- finding minimum: Gradient Descent (a numerical method)
- 請看我自己 愛心的筆記 :)
Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP)
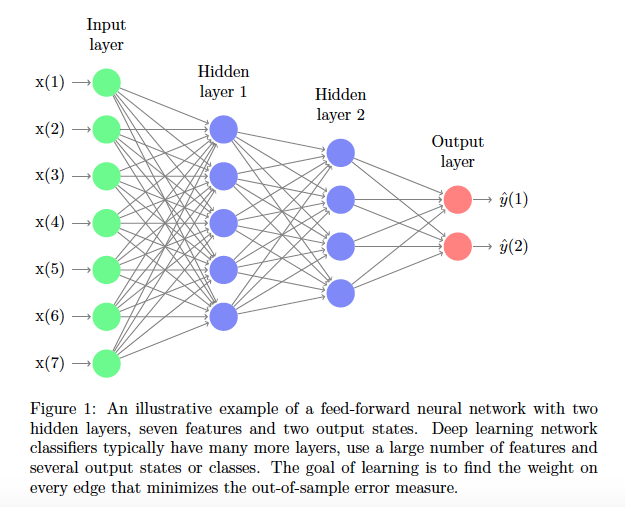
-
Softmax Function: exponentially normalized
-
Example: MLP
Chain Rule in Differential
-
single variable:
y = g(x), z = h(y) Δx -> Δy -> Δz dz/dx = dz/dy * dy/dx -
Backproagation CS231 NN:
Convolution Neural Network (CNN)
- CNN is a nerwork to imitate Human Vision (ANN: Brain or BNN)
- Human vision: Discriminate (ANN: Decide and Learn)
- We
Feature Extraction: Matrix Convolution

convolution 在做 feature extraction
A Complete Example of CNN
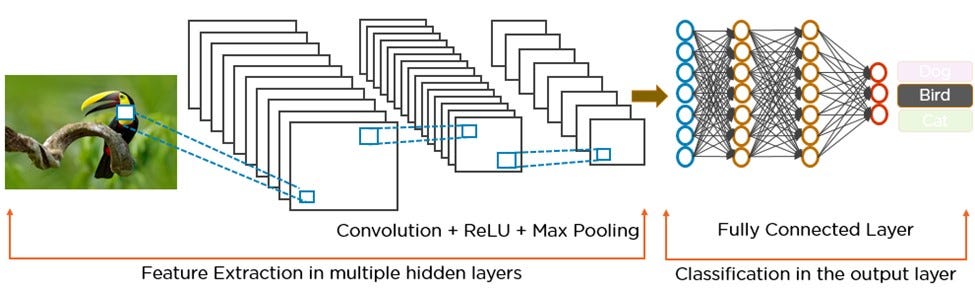
Advanced about Convolution
Classics of CNN
- Yann LeCun
- ImageNet/ ImagesNet Large Scale Visual Recognition
Application of Image Recognition(1/2)
- Object detection
- 分類
Application of Image Recognition(2/2)
- segementation (分割)
- Semantic Segmentation vs. Instance Segmentation
RNN
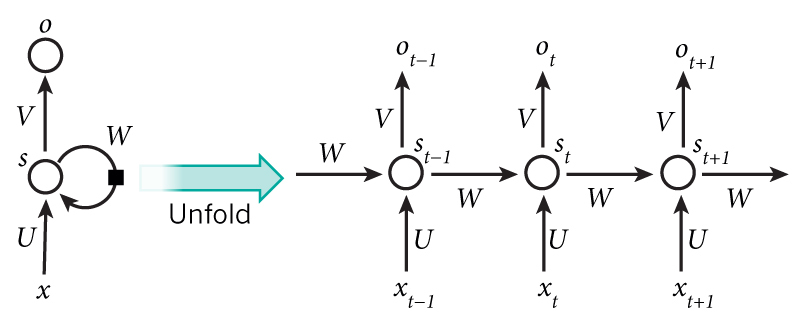
- 模仿人的記憶
- 把前一次的結果記錄起來,下一次 input 併近來一起做運算
RNN 時間有關西,CNN 空間有關西
##LSTM and GRU
- improvement model
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)
- 產生器產生出來,分類器分類出來
- ”” : two models “fights”
Steps of Training
- Step1: Fix generator G , and
Stes of Training
- step2:
DL: NN Models / Flow
-
top-level flow: Model, Data, Problem
-
定義你的問題
Data: Prepare, Pre-process, Analyze
-
70% 以上,都是在處理 data
- prepare
- collect: collect dataset
- label: label expected output for input data
- pre-process
- clean: corrupt, inaccurate, and missing values
- transform: capture the pattern; easy to manipulate
- analyze
- explore: EDA(Explorative Data Analysis) and Visulization
- feature engineering: Encoding and Selection
- pre-process
- split: training set(考古題)/ validation set(練習題)/testing set(大考)
- normalize: feature scaling, standard score
Data Label Problem
data, data, data 很重要!
Enough Data
Enough Labeled Data
Problem Definition
Metrics
Domain Experts
- 回去跟 domain 的人多聊聊!
- 定義一個有意義的問題
AIA: Course
- python:
- 機率與統計
- 機器學習概論(ML)
- 深度學習(DL)
- 卷積神經網路與電腦視覺(CNN/CV)
- RNN
- NLP
- 遷移學習TL(transfeom learning) & 生成對抗網路(GAN)
AI: Boom
- reasons behind the boom
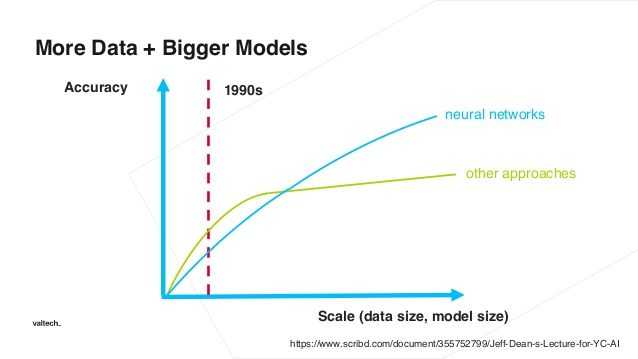
計算複雜度下降 + 計算力的提升 –> 人工智慧的黃金交叉!
- Theories Ready: ANN, DNN, CNN, RNN, RL …
- DNN: Gradient Descent and Backpropagation
- CNN: Convolution and NN-ized
- Hardware Capability: Nvidia GPU + CUDA
- Big Data: ImageNet and ILSVRC
- Software Tools / Communities:
- Open Source
- Theories Ready: ANN, DNN, CNN, RNN, RL …
-
Why DL is hotter than ML ?
-
Software Tools
- Language: python, c++, java
- framework: Tensorflow, keras, pytorch…
- Architecture of Development in DL/ML
- Framework/Package: Tendorflow + keras, PyTorch, CNTK …
- Language: Python
- Environment(Execution): Jupyter(julia, Python, R …)
- Environment(Package): anaconda
- Hardware: local: pc, Cloud (CPU/GPU): Google, …
-
Software Communities
- GitHub:
- type: service, code version control, SCM
- Kaggle:
- type: community and platform for data scientists
- GitHub:
- Type of Applications
- Problem-driven
- EX: AOI (瑕疵檢測)
- Off-the-shelf
- 有套件在那邊了,EX: yolo
- Goal-driven
- Data-driven
- 要有 data 導向思維
- Labor-oriented
Typical Application: 製造業
- 瑕疵檢測
- 預測性維護
- 自動流程控制
- 原料組合最佳化
Challenge from Data - 1
- Data, more data, more labeled data!
- Training data is not the real world => overfitting
- Model is sensitive to minor change of data
Challenge from Data - 2
- 有data,沒技術
- 有技術,沒data
- 有data,有技術:
- 不確定這訓練出來的 model ok?
“Heruistic” and “Empirical”
AI 產業化

- AI infrastucture
- AI Chipset
- AI Consultant
- Product with Ai Functionality
大神們
- Geoffrey Hinton
- British
- Multi-layer neuron network, backpropagation
- Univ. of Toronto.
- Yann LeCun(楊立昆)
- CNN. ML, VS, Robotics
- Yoshua Bengio
大神們們
- 黃仁勳
- 李飛飛
- 吳恩達
AI
-
1980: pc
-
1990: internet
-
2000: Mobile networking
-
2010: AIOT
Trends
Portability
Computing
Networking
New Trends and Others
AI ===> Computing ability
Which solves faster
a top modern algorithm on a 1980s processor or a 1980s algorithm running on a top modern model.
Musical AI
- https://composing.ai/dataset